4. Molecular Compounds
Molecular Models
4. Molecular Compounds
Molecular Models - Video Tutorials & Practice Problems
On a tight schedule?
Get a 10 bullets summary of the topicMolecular Models represent a way to describe the chemical bonds between elements through the use of color-coded balls for elements.
Molecular Models
1
concept
Molecular Models Concept 1
Video duration:
1mPlay a video:
2
example
Molecular Models Example 1
Video duration:
34sPlay a video:
3
Problem
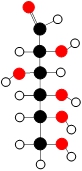
ProblemDetermine the structural formula for the following compound given as a molecular model.
A
C6H12O6
B
C6H12N6
C
C12H6N6
D
C12H6O6
4
Problem
ProblemWhich of the following molecular models represents the ammonia molecule, NH3?
A
B
C
D
Do you want more practice?
We have more practice problems on Molecular Models
Additional resources for Molecular Models
PRACTICE PROBLEMS AND ACTIVITIES (3)
- Sketch the three-dimensional shape of the following molecules: a. Methylamine, CH₃NH₂
- If red spheres represent oxygen atoms, blue spheres represent nitrogen atoms, and all the molecules are gases,...
- If purple spheres represent iodine atoms, white spheres represent hydrogen atoms, and all the molecules are ga...